Readership Map
The readership map above shows the impact of this collection worldwide! To browse the collection, keep scrolling.
About the Collection
The Office of Undergraduate Research (OUR) provides students with the opportunity to present their research at three annual undergraduate research symposia. This collection contains student posters.
-

Geography Illiteracy in America?
Ivan Arrieta and Kimberly Nehls Ph.D.
Since the early 1980s US geographic illiteracy has been a topic of discussion, with some calling it a national security threat. This research will address if Americans are geographic illiterate, and whether geography should be taught more in the school systems in an age of globalization. This research sets out to contribute statistical data on how many UNLV students can guess correct locations compared to people on the Las Vegas Strip. The methodology for this research consisted of randomly asking 100 students at UNLV to identify The United States, an eastern state, and Afghanistan on a map. The same experiment was repeated on the Las Vegas Strip. The experiment at UNLV would test if university students score relatively better than people asked on the Stip. The results from this research show that almost all Americans can locate The United States, less-than half can locate an eastern state, but most could not identify Afghanistan. University students do average better results than people on the Strip as hypothesized. This research shows that most Americans aren’t as geographic illiterate as the media portrays and can find domestic locations, while foreign geographic literacy does seem to lack in comparison. Should geography be taught more as the world becomes more globalized? While it is a good skill to know, I truly think geography isn’t a necessary topic to focus on unless your field benefits from it. Most Americans focus within the general area they’re familiar with and as distance increases Americans become less aware.
-

An Investigation on The History and Current Research of Fragile X Syndrome
Makeda Asare, Isabelle Avenido, and Maxene Vergonia-Fehlman
The purpose of this research is to synthesize the history of Fragile X Syndrome through literature-based research in order to assess the scope of research, population variation, social impact, and treatment. Fragile X was first documented in 1943 by Dr. Julia Bell and Dr. James Purdon Martin in a report of a family case study in which eleven males across two generations showed symptoms of intellectual disabilities. Fragile X Syndrome is an X-linked disorder caused by mutation in the Fragile X mental retardation 1(FMR1) gene on chromosome Xq27.3. The FMR1 mutations are triplet repeat expansion of the CGG repeat sequences in the 5′ untranslated region of the gene, causing hypermethylation of the repeat sequence and the FMR1 promoter. This leads to inactivation of the promoter and loss of the Fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) expression. Because of its X-linked inheritance pattern, males have a higher chance of acquiring this disease than females, with a 1 in 3600 chance and 1 in 6000 chance, respectively. Recent studies attribute FMRP deficiency to neurogenesis changes, lowered glial cell production, and glutamate signaling alteration. Treatment is limited to focusing on managing associated symptoms. Current research emphasizes developing functional therapeutic approaches for treatment. Psychotherapy and various psychotropic medications are applied to target the psychiatric and cognitive features of the disorder. This timeline highlights the ongoing progression of holistic care for FXS patients, supporting the need for well-rounded intervention, spanning from psychotherapy, drug therapies, and wellness checkups.
-

Investigating the Varying Behaviors of Magnesium, Tin, and Lead Oxalate Under High-Pressure
Kevin Ayala Pineda
Recent developments in the field of useful hard x-ray induced chemistry synthesized a novel strontium-based CO derived material under extreme conditions. In hopes of synthesizing this material in larger quantities and in less expensive costs, we report three high-pressure Diamond Anvil Cell investigations on Tin Oxalate (SnC2O4), Magnesium Oxalate (MgC2O4), and Lead Oxalate (PbC2O4) subjected to extreme conditions without the use of hard x-rays. MgC2O4 were acquired up to 25 GPa, with a possible phase transition at 2.4 Gpa. SnC2O4 was pressurized up to 31 GPa inducing irreversible changes in both the Raman spectra and its qualitative properties. Three phase transitions were observed at 2.6 GPa, 15 GPa, and 20 GPa. PbC2O4 was compressed up to 64 GPa, showing very similar behavior as in SnC2O4. Our results demonstrated that each material formed crystallized films after pressurization, which could indicate polymerization of new material(s).
-

Population Changes in the Syrian Arab Republic: 2010-2020
Alessia Borgetti, Chasen Billon, Rylee Gomez, and Kimberley Nehls Ph.D.
This paper intended to study the population-related effects of the Syrian Civil War on the Syrian Arab Republic. The Syrian Civil War that started in March of 2011 is still on-going, along with the associated refugee crisis that arose from it. To determine the extent of the continued crisis, we decided to utilize population data to make inferences related to population growth, decay, and stagnation from the year 2010, through 2020. We found that during the initial stages of the Syrian Civil War, there were significant levels of population decay. However, by as early as 2015, the population decay had slowly begun to lessen, and by 2019, a marginal level of population growth had begun. By 2020, the population growth was nearing pre-war levels, and the level of population growth now makes the Syrian Arab Republic one of the fastest-growing countries worldwide. These findings should allow for a better understanding of the current situation within the Syrian Arab Republic. Particularly, this paper should assist humanitarian groups in understanding where to focus their resources. Additionally, this paper should provide government officials the data necessary to re-shape their policies towards refugee assistance and foreign aid.
-

Resilience in the BIPOC community: A systematic review
Lianelys Cabrera Martinez, Aldo Barrita B.A., and Gloria Wong-Padoongpatt Ph.D.
The present study is a systematic literature review on the psychology of resilience, or the ability to bounce back after a difficult situation. Although resilience is a timely and relevant variable in social psychology, little is known about its connection to the racism-related experiences of Black, Indigenous, and People of Color (BIPOC). This review explores how resilience manifests in the BIPOC community and its influence on the identity of minority groups. Previous research has shown that BIPOC reports higher resilience; however, there is still uncertainty around its connection to discrimination. Through the analysis of nine final research articles, we examined four main questions: (a) What is the prominent definition of resilience?, (b) How is resilience experienced or manifested among BIPOC?, (c) How is resilience operationalized when experiencing oppression?, and (d) What are the limitations in the literature of resilience? Results shed light on the need to further investigate resilience as a protective factor against discrimination in the BIPOC community.
-

Zeolite/ZVI System TOF The Treatment of Nutrients in Urban Runoff
Tremyia Campbell, Jasminn Gray, Joe C. Costa Rodriguez, and Jacimaria Ramos Batista Ph.D.
Algal blooms have taken place in Lake Mead, Nevada, and a major bloom occurred in 2001. One reason for algal blooms at Lake Mead is excess of nutrients from runoff water discharge during rainy seasons. Algal blooms in lakes and rivers are a sign of eutrophication - an excessive growth of plant life that leads to death of animal life from lack of oxygen. In addition, algal blooms impact the use of water as a drinking source because of the presence of algal toxins. Nutrients that cause algae bloom include ammonia, nitrate, and phosphorus. The objective of this research is to implement a passive system that removes nutrients from runoff water. If successful, such a system could be integrated into runoff street gutters to remove nutrients.
To test the viability of this system, a dual-media consisting of zero-valent iron (ZVI) and zeolite, was built. A synthetic runoff water solution is fed to the columns using a peristaltic pump. The synthetic runoff water composition mimics that of a typical runoff in Las Vegas. The system can be operated at retention times of 30 -180 minutes. The influent and effluent water to the column are sampled daily and the concentration of nitrate, phosphorus, and ammonia are analyzed to determine the effectiveness of the system. It is expected that ammonia will be removed in the zeolite and nitrate will be reduced by ZVI. In addition, microbes growing on the media might be able to remove phosphorus.
-

Lead Levels in Rodents Residing on Shooting Ranges
Bijoux Cheun, Maria Martinez, and Sean A. Neiswenter Ph.D.
The objective of this study is to investigate the effects that lead left at shooting ranges have on local rodent populations. Shooting ranges have been shown by previous research to have a great influence on the level of lead present in nearby soils and plants. This lead contamination has also been shown to have serious consequences for fauna residing near these ranges, ranging from lead toxicity to death. Many shooting ranges exist in Southern Nevada, and we have sampled a small number of these ranges to explore the possible effects they have on nearby rodent populations. The livers of Dipodomys merriami were sampled. We intend to sample additional species and consider life histories in relation to levels of lead toxicity.
-

Recycling Methods for MAPbI3 Perovskite Solar Cells
Donald Chicas and Shubhra Bansal Ph.D.
Halide perovskite solar cells (HPSCs) are a promising renewable energy technology due to their high efficiency and large-scale processing. Many HPSCs utilize lead, presenting health, environmental, and regulatory issues. To mitigate these issues, recycling processes for HPSCs have been researched. This mitigates the risk of lead leakage into the environment while reducing the cost of HPSCs over time. The current methodologies of recycling HPSCs will be reviewed, scrutinizing how recovered lead can be used to manufacture PSCs. To evaluate the efficacy of these recycling methods, the material recoverability and recycled device performance will be considered. Through this, recycling methods that yield high purity precursors for the manufacture of HPSCs will be proposed.
-
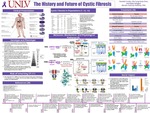
The History and Future of Cystic Fibrosis
Randall Combs, Che Fung Andy Chan, and Daisy Sahagun
The purpose of this research timeline is to highlight the tumultuous yet inspiring history of Cystic Fibrosis disease and treatment to give us a more pragmatic understanding of its current state. Cystic Fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disease, most often caused by a single amino-acid deletion of phenylalanine at position 508 in the nucleotide binding domain, which results in a loss of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Symptomatology varies considerably but a buildup of mucus in the respiratory tract leading to lung failure, and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency which results in digestive and metabolic dysfunction are commonly, if not ubiquitously present in homozygous CF patients. In 1962, the prognosis of Cystic Fibrosis was grim and had a median survival age of just ten years old. Among the first treatments of this disease was a procedure called ‘postural drainage’ in which children were turned upside down to allow the excessive mucus buildup in their lungs to exit. Now, not only has generalized medical care improved but as with most genetic diseases, a comprehensive understanding of the exact biochemical defect has yielded therapeutics that can address the root issue rather than solely mitigate symptoms – drugs such as ivacaftor and lumacaftor aim to do just that. This timeline serves as an effort to synthesize the discoveries and breakthroughs that have altered CF treatment for the better and looks to the future for what type of life patients affected by this genetic illness might reasonably expect.
-

Retinoblastoma: Past, Present, and Future
Izabela Daneva, Crysty-Ann Olaco, and Albert Tran
The purpose of this research timeline is to synthesize the natural history of retinoblastoma to understand its societal effects and develop a public health message to raise awareness of the disease. We used literature-based research in order to gain an understanding about the discovery of this disease and investigate its most current state of knowledge. Retinoblastoma is an intraocular cancer that manifests early in childhood. It is typically linked to a somatic or germline insertion, deletion, or single-base substitution mutation on both alleles of RB1, a tumor-suppressor gene. Retinoblastoma was first identified in 1809 by James Wardrop, and since then, research has been focused on improved treatment methods to prevent enucleation and has been steady with focus on the RB1 allele. Retinoblastoma is characterized by many assorted phenotypes that vary in severity based on the size of the chromosomal deletion. The most common symptoms include leukocoria, poor vision tracking, swelling and inflammation, all of which can be treated upon early detection. Methods of treatment include enucleation that completely removes the eye with the tumor, leaving the muscles and orbital contents intact, and it is 95% effective. Chemotherapy is also used in severe cases. The discovery of the Rb1 gene has had significant impacts with the advancement of cancer research. Because of this, mutations in the Rb gene are vastly studied due to the association of Rb in other cancers and its molecular action in the cell cycle. It is often taught in foundational biology courses, as a result.
-

Visual Attention During Observational Learning of Motor Skills: Implications in Rehabilitation After Amputation
Briauna Davis and Szu-Ping Lee Ph.D.
It is difficult to stop accidental falls and maintain balance after leg amputation. The goal of post-amputation rehabilitation is to improve mobility function, reduce fall risks, and improve safety. Although there have been advancements in prosthetic technology, individuals with leg amputation are still experiencing frequent falls. We believe this is partially due to the lack of scientific knowledge on prosthetic skill learning after amputation. Post-amputation rehabilitation involves learning and relearning complex motor skills, such as walking and quick stepping to stop falls. This process becomes intense as Individuals perform these tasks with a prosthesis. Our goal was to find a way to make rehabilitation training after amputation more effective. This study examines the effectiveness of incorporating peer-based training during post-amputation rehabilitation. Participants with lower limb amputation will be instructed to watch video demonstrations of balance and recovery tasks performed by an amputee peer or non-amputee. The performance of participants will be tracked before, throughout, and after training. Knowledge from this study will benefit individuals with lower limb amputation by speeding up the learning of prosthetic skills lower limb amputation.
-

Damaging Tobacco Mosaic Virus Using Electrochemistry: A Novel Method to Synthesize High-Quality Vaccines
Angelica Diaz Tremillo, Kevin Ayala Pineda, Nicholas Pudar, Drake Joseph, and Michael Pravica
As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, it is imperative to develop novel and rapid ways to synthesize highly targeted and effective vaccines. We report a study that tested the effectiveness of using electrochemistry to damage the Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV). We hypothesized that by utilizing the acidic properties of DNA and RNA contained by viruses, viral genetic material can be selectively denatured using electrochemistry. We also hypothesized that the viral capsid would be less damaged due to its non-acidic properties and thus the intact capsid could be used as a vaccine vector to promote immune system response. We tested TMV potency by infecting pinto bean seedlings with electrochemically treated and untreated TMV and observed their growth for four weeks. Various spectroscopic techniques such as Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) and Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy were implemented to assess changes in the electrochemically-treated viruses. Finally, Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) was used to examine oxidative damage in the samples. It was observed that plants infected with electrochemically-treated TMV developed significantly fewer necrotic lesions compared to plants infected with untreated TMV. We also found significant changes in the UV-Vis spectral peaks, NMR spectral peaks, and cyclic voltammograms before and after electrochemical damage. Preliminary results were obtained which suggest that the electrochemical techniques used in this study effectively damaged the TMV virions. Through further testing and improvements, this innovative technique could be used to develop highly targeted and effective vaccines.
-

Modeling COVID-19 Infection Rates using SIR and ARIMA Models
Janelle Domantay, Ilya Pivavaruk, and Victor Taksheyev
With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, it has become of increasing interest to both monitor and predict the growth of its infection rates. In order to analyze the accuracy of epidemiological prediction, we consider two different models for prediction, the Susceptible Infected and Removed (SIR), and Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) models. Using a dataset of Clark County COVID-19 infections, we create various ARIMA and SIR models that attempt to predict the progression of COVID-19 infections whilst comparing these predictions to the dataset. We observed that the ARIMA model performed more accurately overall, having a much lower Root Mean Squared Error than its counterpart.
-

Cultural Identity Predicts Resilience in Maltreated Youth
Jordan Donohue, Janelle Salcedo, James Webster, and Kinsey Ellis
Literature suggests that a stronger sense of cultural identity predicts higher levels of resilience following a traumatic event. However, there are limited studies that examine this relationship in children. The present research analyzes the relationship between cultural identity and resilience in a sample of maltreated youth. Participants included youth (n=65) aged 11-17 years in Department of Family Services (DFS) custody following removal from their home after substantiated child maltreatment. Cultural identity and resilience were both assessed by the Nevada Child and Adolescent Needs and Strengths (NV- CANS). A linear regression indicated a significant predictive relationship between cultural identity and resilience, F (1, 63) = 16.073, p=.001. Results suggest that 20.3% (Adjusted R² = 19.1%) of the variance in resilience could be explained by the variance in cultural identity. Specifically, according to the unstandardized regression coefficients, an increase in cultural identity predicted an increase in resilience (B =.322, SEculturalidentity = 0.08, t = 4.009, p=.001, 95% CI [.161, .482]). Overall, these findings suggest that cultural identity predicts levels of resilience in maltreated youth. This is a critical finding in expanding the literature and improving clinical outcomes, suggesting clinicians should take cultural factors into consideration and work with youth to build cultural support networks and a sense of belonging.
-

A Mediation Analysis of Racial Microaggressions, Poor Coping Mechanisms and Mental Health
Janelle Ferraris, Andrea Galdamez, Aldo Barrita, and Kristin Vierra
Microaggressions are daily slights and denigrations perpetrated towards marginalized individuals. These invalidations are perceived as significant stressors for marginalized people. The bulk of research on microaggressions indicates that these everyday slights can have a negative impact on mental health. The current study examines the relationship between microaggressions, detachment internalized racism, and negative mental health symptoms of depression, anxiety and depression. Specifically, regression analysis was used to investigate the hypothesis that both internalization and detachment mediate the effect of microaggressions on poor mental health symptoms for PoC. Results indicated that for PoC, microaggressions was a significant predictor of symptoms of both internalization, B = .071, SE = .021, p = .000, and detachment B = .276, SE = .029, p = .000. Additionally both internalization B = .389, SE = .070, p = .000 and detachment B = .869, SE = .082, p = .000 were a significant predictor for poor mental health symptoms. Results support a partial mediational hypothesis. Microaggression was a significant predictor of poor mental health even when controlling for both mediators, B = .285, SE = .042, p = .000. Approximately 26% of the variance in satisfaction was accounted for by the predictors (R2 = .261). The procedure yielded a significant coefficient, B = .182, SE = .038, p = .000 with 95% bias corrected confidence intervals that did not include zero [.108, .256]. These results suggest that racial discrimination experienced by PoC exposes them to higher risks of both poorer mental health and negative coping mechanisms.
-

Predicting Variant Pathogenicity with Machine Learning
Zachary Fitzhugh, Martin R. Schiller Ph.D., and Fatma Nasoz
There are roughly 22,000 protein-coding genes in the human body, many of which play important roles in biological functions. The proteins fold in 3D space, and this is most often necessary for function. A genetic variant can disrupt the secondary structure of a protein (one aspect of structure) or eliminate a site important in protein-protein interaction or post-translational modification. The loss of function or deregulation can result in disease. Thus, there is great biomedical interest in identifying disease-causing single-nucleotide variants.
We hypothesize that we can accurately predict variant pathogenicity. We used machine learning to predict the pathogenicity of a set of 28,369 single-nucleotide variants across 10 genes. The data are acquired from publicly available saturation mutagenesis data sets, which generate every possible amino acid substitution at every position in a protein. Our approach employs a support vector machine using linear, polynomial, and RBF kernel functions. The problem is implemented as a binary classification problem, where a label of 1 indicates a disease-causing variant and a label of 0 indicates a benign variant. The model predicts pathogenicity based on amino acid, post-translational modification, and secondary structure information. We cleaned and analyzed the data with custom Python scripts. Our results show average balanced accuracy scores for classifying pathogenicity of approximately 57.9%, 60.3%, and 60.3% for the linear, polynomial, and RBF kernels, respectively. Therefore, the model is an improvement over random guessing but has room for improvement.
-

Teachers' Experience with Lack of Resources in Classrooms
Susan Florian and Magdalena Martinez Ph.D.
Teachers that are working in Nevada are experiencing problems with insufficient materials. The overall purpose of this study is to provide information about their struggles with materials in the Clark County School District. What are teachers' experiences with shortages of resources, and how does it impact their teaching strategies? Teachers' experiences are important to note. Their experiences matter in finding the problems they face is essential to aid them with suitable materials. Finding solutions to their needs will improve their teaching strategies and personal spending, but children will also get the proper materials they deserve. The selection was composed of three different teachers from three different schools within the Clark County School District. This study generates a qualitative understanding of teachers' experiences. Most teachers explained the different levels of frustration with the administration and the lack of resources they experienced. Analysis shows that this increases stress levels, personal spending, and teacher attrition. These methods and responses should help the administration improve the school system and express their employee's concerns to decision-makers to receive the proper and necessary resources. Certain limitations to this study are important to note, but the overall evidence proves that these problems negatively impact teachers' experiences.
-

Neurofibromatosis 1: Discovery, Treatment and Social Impact
Betsua Garcia and Arsen Khachatryan
The purpose of this timeline research project is to provide an outline of the discovery of Neurofibromatosis 1 to identify gaps in knowledge. Frederick von Recklinghausen is credited with the disease’s classification in 1882 when he observed two different cases of patients with neurofibromas. Current research of the disease involves its characterization at a molecular and genetic level. The symptoms of the disease include non-cancerous tumors in the nervous system (neurofibromas) and optic nerves (optic nerve gliomas), as well as cafe-au-lait spots around the axillary and groin areas. It tends to occur in 1 out of 3,000 births globally without distinction between sexes and racial groups, but the frequency and severity of certain symptoms vary across different races. In the past, curative treatments for neurofibromatosis 1 were unavailable, but palliative care has been provided through chemotherapy, radiation treatments, and surgical procedures to remove tumors. However, in April 2020, a new treatment called Koseulgo (selumetinib) that stops the growth of tumors by blocking key enzymes was approved by the FDA and is one of the first curative treatments developed. The disease also seems to have other impacts on social and emotional wellbeing on patients and their families. Therefore, support services that can help patients and their families develop appropriate coping skills, and the further development of palliative care to ease the severity of symptoms, may prove to be beneficial. In conclusion, this timeline of Neurofibromatosis 1’s discovery helps provide context for its characterization and contributes to the ongoing research.
-

Frequency of Each Sex Affected by Sudden Unexplained Deaths due to Developmental Epilepsy
Betsua Garcia-Trujillo, Dustin Hines Ph.D., Jeffrey Barker, and Rochelle Hines Ph.D.
Developmental epilepsy is a group of neurodevelopmental disorders that is mainly characterized by the onset of different types of seizures, developmental delays, and electroencephalogram (EEG) changes at a young age. Because it can describe a variety of syndromes, symptoms and specific causes may vary between affected individuals. Previous research has examined sex differences within affected adult populations but research examining sex differences for developmental epilepsy is lacking.
The objective of this research is to determine the frequency of each sex within a population of mice that died prematurely from developmental epilepsy due to mutations of the GABAA receptor α2 subunit.
To determine the frequency of each sex, we extracted DNA from the tails of pups that died prematurely. We determined their sex by running PCR to amplify the sex-determining region on the Y chromosome (SRY). PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. Males are identified by the presence of two bands of 300 and 350 base pairs (bp) while females are identified by one single band of 350 bp.
Current research provides evidence that males are at higher risk for sudden unexplained death in epilepsy (SUDEP). The current study aims to examine whether males are at higher risk in our model of developmental epilepsy. Future research can provide additional insight into the mechanisms that lead to differences in SUDEP risk.
-
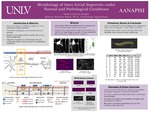
Morphology of Axon Initial Segments under Normal and Pathological Conditions
Betsua Garcia-Trujillo and Rochelle Hines Ph.D.
The Axon Initial Segment (AIS) is a compartment within the neuron that plays a major role in the initiation of action potentials. Changes to AIS length and position can alter the probability of action potential firing. A majority of modeling studies consider the AIS to have linear morphology; however, we have observed different AIS shapes in different pathological conditions.
The objective of this research is to classify AISs by shape (straight, curved, or kinked) and to determine the frequency of each shape across normal and pathological conditions.
We stained AISs in cortical tissue using immunohistochemistry and imaged them with a confocal microscope. After imaging, we qualitatively categorized AISs in normal and pathological samples based on their shape and plotted them in ImageJ to obtain numerical data (Cartesian coordinates).
We have compared AISs in cortical tissue from wild type mice to those from the Mecp2+/- model of Rett syndrome. We plan to use the Cartesian data to develop a model that describes the linear and non-linear morphologies of the AIS.
Although previous research has demonstrated that position, composition, and length of AISs helps determine neuronal excitability, the relationship between AIS shape and pathology has not been examined. The current study helps establish AIS morphology as a possible pathological feature that may have functional consequences, and future experiments will investigate a relationship between AIS shape and neuronal excitability. Additional research may help to gain a deeper understanding of normal and pathological development and may lead to the development of new treatments.
-
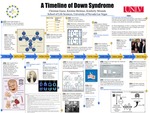
A Timeline of Down Syndrome
Christian Guese, Kristina McInnes, and Kimberly Miranda
The purpose of this research timeline is to synthesize the natural history of Down Syndrome (DS) to discover absence of knowledge, discuss the bioethics in prenatal screening and develop a public health message. Our method of research was literature-based. DS is one of the most common aneuploidy disorders in the United States. There are three genetic variations of DS, Trisomy 21, a third copy of chromosome 21, accounts for 95% of cases. DS causes intellectual disability, developmental delays, facial dysmorphia, and low muscle tone. DS also leads to an increased risk for congenital heart defects and Alzheimer’s disease later in life. In 1866, John Langdon Down was the first to link the physical characteristics of individuals with DS. Although sentiment towards DS was not positive initially, we now have a greater understanding of the disorder and have more humane treatments. In earlier years, doctors were advocating to parents to cease caring for their child with DS, including institutionalizing them. Throughout the years, leaders began advocating for DS, such as John F. Kennedy; in 1962 he established the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) to support and research mental disabilities. The improved medical care and social inclusion is making positive impacts on the physical and intellectual development of individuals with DS. The life expectancy for a person with DS increased after eradicating inhumane practices, which is why it’s important to develop a public health message promoting social advocacy and public health awareness.
-

Study of Sickle Cell Disease
Aaron Guevarra, Carlos Herrera, and Faysal Ali
The purpose of this research timeline is to explore the history, prevalence, and effects of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) so that treatments and possible future experiments or cures may be discussed. In SCD, abnormal red blood cells appear as sickle shaped as opposed to the round shape of normal red blood cells. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, so an individual must inherit two copies of the allele. The gene mutation is a single nucleotide mutation in the gene which codes for β-globin. In 1910, James B. Herrick first described the disease, and in 1949, its inheritance pattern was determined. It can cause an array of complications due to the loss of blood cells and restricted blood flow. Carriers with only one copy of the disease-causing allele exhibit sickle cell trait, which does not result in the same severe symptoms that sickle cell disease does. SCD is prevalent in areas stricken by malaria, as sickle cell trait confers some resistance to the pathogen. The social impacts of SCD are majorly based on financial costs and quality of life. Patients also suffer from physiological and psychological impacts. Treatments are divided into three parts: supportive care therapies such as fever management, disease-modifying therapies such as the medicine Hydroxyurea, and blood transfusion. Future research on SCD is based on improving and finding new curative therapies to completely cure SCD such as Hematopoietic stem cell transplant and gene therapy.
-

Unsustainable Fast Fashion in the United States
Itzel Gutierrez and Kimberly Nehls Ph.D.
My research will be focused on how unsustainable fast fashion is killing the ecosystem, whether or not it is bad for the environment and what percentage of it ends up in landfills? Boohoo, Shein and PrettyLittleThing are popular fast fashion retail apps among U.S consumers, cheap fast fashion tends to encourage consumers to over buy. My research will start with where does fast fashion come from and where does it end up? Fast fashion is based on trends going on in the red carpet, fashion shows or influenced by social media. Throwing away clothes because it is out of style should never be an option. Once people are done with a piece of clothing, they can give away their items, donate to thrift stores, or even resell their items. My research will explore ways on what consumers can do to decrease the percentage of fast fashion that ends up in landfills. The top 10 worst fabrics for the environment include cotton, polyester, nylon, acrylic, viscose, bamboo, acetate, and wool. These fabrics are considered bad for the environment because they do not completely break down and some micro plastics can make their way into the ocean and soil. One way to stop putting the blame on consumers is for brands to become more aware about how what they are doing and making is affecting the environment.
-

Introduction to Quantum Computing and Information
Rashad C. Hall and Bernard Zygelman Ph.D.
The world is constantly challenged by complex scientific, economic, and medical problems, etc. In many cases, progress in finding solutions requires the application of modern computing machines. At the same time, the classical paradigm based on the Turing machine model has well-known limits. Some problems require computing resources that grow exponentially with the size of data, thus making solutions intractable for such applications. In the past 25 years, researchers have realized that computing machines based on the principles of quantum mechanics might offer a novel strategy for attacking these problems. In this report, we investigate how quantum and classical computers differ. To highlight these differences, we performed several experiments designed and implemented on an IBM quantum computer. In one circuit design, we investigated the measurement outcomes when a quantum system in each state, represented by the symbol |0>, is processed by a Hadamard gate. We noticed specific patterns in measurement outcomes when employing an odd and even number of Hadamard gates. For every odd number of H-gates used, we observed two distinct measurement outcomes 0,1 that were distributed with a 50% chance for each. Results suggests that a Hadamard gate is a so-called noisy gate; in the same way, flipping a coin result in two evenly distributed outcomes. If that interpretation is correct, one expects the same outcomes for an even number of gates. We resolve this paradox by positing that a quantum state can exist in a so-called superposition state, allowing for the interference of probability amplitudes.
-

The Analysis of VR/AR Cost and Immersion
Yessenia Henriquez and Si Jung Kim Ph.D.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) habitually seek to construct new environments to produce virtual experiences. Virtual experiences are unimaginable to establish in real life, but not in a digital context. These virtual experiences could range from medical procedures in a virtual hospital setting to bizarre worlds in entertainment environments. Nonetheless, the rudimentary necessity to fabricate genuine virtual experiences is immersion. This literature review centers around discovering various aspects that formulate both augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). This study attempts to comprehend the possibilities and objectives that AR and VR are most compatible with. The upcoming results heavily touch upon immersion (genuine virtual experiences) and cost (physical or software cost) in VR/AR. Overall, VR structures are more immersive to the user in integrating an “out of body” experience but are often more costly due to the equipment needed to perform these computations. AR structures are more available to cheaper alternatives but do not create a serious virtual experience (VE) as VR structures. Both VR and AR environments and objectives, however, combine interdisciplinary areas for a dynamic VE for users.